PROTECT Study: The head-to-head superiority trial that studied dual-pathway FILSPARI® vs single-pathway RASi1,2
Study design1,3,4

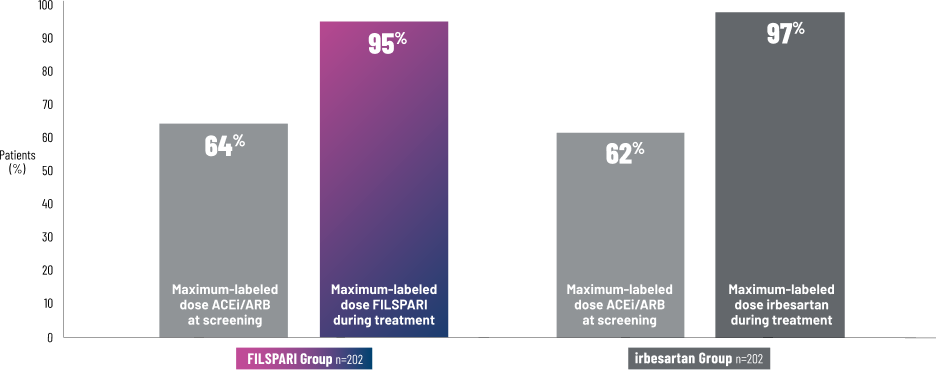
FILSPARI is the only IgAN treatment studied vs a maximum-labeled-dose active comparator1,5
The PROTECT Study compared FILSPARI to irbesartan at maximum-labeled doses2
- Baseline eGFR: 57 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Median UPCR: 1.2 g/g
- Hematuria: 56% of patients
- History of diabetes or impaired fasting glucose: 11% of patients
- History of hypertension: ~78% of patients
- Sex: 70% male
- Ethnicity: 67% White, 28% Asian, 1% Black or African American
- Age: Mean, 46 years (range, 18-76)
- Biopsy-proven IgA nephropathy
- Proteinuria ≥1 g/d
- eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Systolic BP ≤150 mmHg and diastolic BP ≤100 mmHg at screening
- Maximum-tolerated dose of RASi treatment that was at least 50% of maximum-labeled dose for at least 12 weeks prior to screening
- Patients with other glomerulopathies or those who had been recently treated with systemic immunosuppressive medications (including corticosteroids) for >2 weeks within 3 months of screening
- IgA nephropathy secondary to another condition or Henoch-Schönlein purpura
- Presence of cellular glomerular crescents in >25% of glomeruli on renal biopsy within 6 months of screening
- Chronic kidney disease in addition to IgA nephropathy
- History of organ transplantation, with exception of corneal transplants
- Patients who are pregnant, planning to become pregnant during the course of the study, or breastfeeding
See proteinuria and eGFR results from the head-to-head PROTECT trial.
See the safety results from the 2-year clinical trial.
ACEi=angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB=angiotensin receptor blocker; BP=blood pressure; eGFR=estimated glomerular filtration rate; IgA=immunoglobulin A; IgAN=immunoglobulin A nephropathy; RASi=renin-angiotensin system inhibitor; SOC=standard of care; UPCR=urine protein-to-creatinine ratio.
References:
INDICATIONS & USAGE
FILSPARI® (sparsentan) is indicated to slow kidney function decline in adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) who are at risk for disease progression.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY AND EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
Because of the risks of hepatotoxicity and birth defects, FILSPARI is available only through a restricted program called the FILSPARI REMS. Under the FILSPARI REMS, prescribers, patients and pharmacies must enroll in the program.
Hepatotoxicity
Some Endothelin Receptor Antagonists (ERAs) have caused elevations of aminotransferases, hepatotoxicity, and liver failure. In clinical studies, elevations in aminotransferases (ALT or AST) of at least 3-times the Upper Limit of Normal (ULN) have been observed in up to 3.5% of FILSPARI-treated patients, including cases confirmed with rechallenge.
Measure transaminases and bilirubin before initiating treatment and monthly for the first 12 months, and then every 3 months during treatment. Interrupt treatment and closely monitor patients who develop aminotransferase elevations more than 3x ULN.
FILSPARI should generally be avoided in patients with elevated aminotransferases (>3x ULN) at baseline because monitoring for hepatotoxicity may be more difficult and these patients may be at increased risk for serious hepatotoxicity.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
FILSPARI can cause major birth defects if used by pregnant patients based on animal data. Therefore, pregnancy testing is required before the initiation of treatment, during treatment and one month after discontinuation of treatment with FILSPARI. Patients who can become pregnant must use effective contraception before the initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for one month after discontinuation of treatment with FILSPARI.
Contraindications
FILSPARI is contraindicated in patients who are pregnant. Do not coadminister FILSPARI with angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), ERAs, or aliskiren.
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Elevations in ALT or AST of at least 3-fold ULN have been observed in up to 3.5% of FILSPARI-treated patients, including cases confirmed with rechallenge. While no concurrent elevations in bilirubin >2-times ULN or cases of liver failure were observed in FILSPARI-treated patients, some ERAs have caused elevations of aminotransferases, hepatotoxicity, and liver failure. To reduce the risk of potential serious hepatotoxicity, measure serum aminotransferase levels and total bilirubin prior to initiation of treatment and monthly for the first
12 months , then every3 months during treatment.Advise patients with symptoms suggesting hepatotoxicity (nausea, vomiting, right upper quadrant pain, fatigue, anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, fever, or itching) to immediately stop treatment with FILSPARI and seek medical attention. If aminotransferase levels are abnormal at any time during treatment, interrupt FILSPARI and monitor as recommended.
Consider re-initiation of FILSPARI only when hepatic enzyme levels and bilirubin return to pretreatment values and only in patients who have not experienced clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Avoid initiation of FILSPARI in patients with elevated aminotransferases (>3x ULN) prior to drug initiation because monitoring hepatotoxicity in these patients may be more difficult and these patients may be at increased risk for serious hepatotoxicity.
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: FILSPARI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant patient and is contraindicated during pregnancy. Advise patients who can become pregnant of the potential risk to a fetus. Obtain a pregnancy test prior to initiation of treatment with FILSPARI, monthly during treatment, and one month after discontinuation of treatment. Advise patients who can become pregnant to use effective contraception prior to initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for one month after discontinuation of treatment with FILSPARI.
- FILSPARI REMS: Due to the risk of hepatotoxicity and embryo-fetal toxicity, FILSPARI is available only through a restricted program called the FILSPARI REMS. Prescribers, patients, and pharmacies must be enrolled in the REMS program and comply with all requirements (www.filsparirems.com).
- Hypotension: Hypotension has been observed in patients treated with ARBs and ERAs. There was a greater incidence of hypotension-associated adverse events, some serious, including dizziness, in patients treated with FILSPARI compared to irbesartan. In patients at risk for hypotension, consider eliminating or adjusting other antihypertensive medications and maintaining appropriate volume status. If hypotension develops, despite elimination or reduction of other antihypertensive medications, consider a dose reduction or dose interruption of FILSPARI. A transient hypotensive response is not a contraindication to further dosing of FILSPARI, which can be given once blood pressure has stabilized.
- Acute Kidney Injury: Monitor kidney function periodically. Drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) can cause kidney injury. Patients whose kidney function may depend in part on the activity of the RAS (e.g., patients with renal artery stenosis, chronic kidney disease, severe congestive heart failure, or volume depletion) may be at particular risk of developing acute kidney injury on FILSPARI. Consider withholding or discontinuing therapy in patients who develop a clinically significant decrease in kidney function while on FILSPARI.
- Hyperkalemia: Monitor serum potassium periodically and treat appropriately. Patients with advanced kidney disease, taking concomitant potassium-increasing drugs (e.g., potassium supplements, potassium-sparing diuretics), or using potassium-containing salt substitutes are at increased risk for developing hyperkalemia. Dosage reduction or discontinuation of FILSPARI may be required.
- Fluid Retention: Fluid retention may occur with ERAs, and has been observed in clinical studies with FILSPARI. FILSPARI has not been evaluated in patients with heart failure. If clinically significant fluid retention develops, evaluate the patient to determine the cause and the potential need to initiate or modify the dose of diuretic treatment then consider modifying the dose of FILSPARI.
Most common adverse reactions
The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) are hyperkalemia, hypotension (including orthostatic hypotension), peripheral edema, dizziness, anemia, and acute kidney injury.
Drug interactions
- Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Inhibitors and ERAs: Do not coadminister FILSPARI with ARBs, ERAs, or aliskiren due to increased risks of hypotension, syncope, hyperkalemia, and changes in renal function (including acute renal failure).
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use of FILSPARI with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, interrupt FILSPARI treatment. When resuming treatment with FILSPARI, consider dose titration. Monitor blood pressure, serum potassium, edema, and kidney function regularly when used concomitantly with moderate CYP3A inhibitors. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increases sparsentan exposure which may increase the risk of FILSPARI adverse reactions.
- Strong CYP3A Inducers: Avoid concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inducer. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inducer decreases sparsentan exposure which may reduce FILSPARI efficacy.
- Antacids and Acid Reducing Agents: Administer FILSPARI 2 hours before or after administration of antacids. Avoid concomitant use of acid reducing agents (histamine H2 receptor antagonist and PPI proton pump inhibitor) with FILSPARI. Sparsentan exhibits pH-dependent solubility. Antacids or acid reducing agents may decrease sparsentan exposure which may reduce FILSPARI efficacy.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (NSAIDs), Including Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Inhibitors: Monitor for signs of worsening renal function with concomitant use with NSAIDs (including selective COX-2 inhibitors). In patients with volume depletion (including those on diuretic therapy) or with impaired kidney function, concomitant use of NSAIDs (including selective COX-2 inhibitors) with drugs that antagonize the angiotensin II receptor may result in deterioration of kidney function, including possible kidney failure.
- CYP2B6, 2C9, and 2C19 Substrates: Monitor for efficacy of concurrently administered CYP2B6, 2C9, and 2C19 substrates and consider dosage adjustment in accordance with the Prescribing Information. Sparsentan decreases exposure of these substrates, which may reduce efficacy related to these substrates.
- P-gp and BCRP Substrates: Avoid concomitant use of sensitive substrates of P-gp and BCRP with FILSPARI. Sparsentan may increase exposure of these transporter substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
- Agents Increasing Serum Potassium: Monitor serum potassium frequently in patients treated with FILSPARI and other agents that increase serum potassium. Concomitant use of FILSPARI with potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, potassium-containing salt substitutes, or other drugs that raise serum potassium levels may result in hyperkalemia.
Please see the full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING, for additional Important Safety Information.
INDICATIONS & USAGE
FILSPARI® (sparsentan) is indicated to slow kidney function decline in adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) who are at risk for disease progression.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY AND EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
Because of the risks of hepatotoxicity and birth defects, FILSPARI is available only through a restricted program called the FILSPARI REMS. Under the FILSPARI REMS, prescribers, patients and pharmacies must enroll in the program.
Hepatotoxicity
Some Endothelin Receptor Antagonists (ERAs) have caused elevations of aminotransferases, hepatotoxicity, and liver failure. In clinical studies, elevations in aminotransferases (ALT or AST) of at least 3-times the Upper Limit of Normal (ULN) have been observed in up to 3.5% of FILSPARI-treated patients, including cases confirmed with rechallenge.
Measure transaminases and bilirubin before initiating treatment and monthly for the first 12 months, and then every 3 months during treatment. Interrupt treatment and closely monitor patients who develop aminotransferase elevations more than 3x ULN.
FILSPARI should generally be avoided in patients with elevated aminotransferases (>3x ULN) at baseline because monitoring for hepatotoxicity may be more difficult and these patients may be at increased risk for serious hepatotoxicity.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
FILSPARI can cause major birth defects if used by pregnant patients based on animal data. Therefore, pregnancy testing is required before the initiation of treatment, during treatment and one month after discontinuation of treatment with FILSPARI. Patients who can become pregnant must use effective contraception before the initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for one month after discontinuation of treatment with FILSPARI.
Contraindications
FILSPARI is contraindicated in patients who are pregnant. Do not coadminister FILSPARI with angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), ERAs, or aliskiren.
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Elevations in ALT or AST of at least 3-fold ULN have been observed in up to 3.5% of FILSPARI-treated patients, including cases confirmed with rechallenge. While no concurrent elevations in bilirubin >2-times ULN or cases of liver failure were observed in FILSPARI-treated patients, some ERAs have caused elevations of aminotransferases, hepatotoxicity, and liver failure. To reduce the risk of potential serious hepatotoxicity, measure serum aminotransferase levels and total bilirubin prior to initiation of treatment and monthly for the first
12 months , then every3 months during treatment.Advise patients with symptoms suggesting hepatotoxicity (nausea, vomiting, right upper quadrant pain, fatigue, anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, fever, or itching) to immediately stop treatment with FILSPARI and seek medical attention. If aminotransferase levels are abnormal at any time during treatment, interrupt FILSPARI and monitor as recommended.
Consider re-initiation of FILSPARI only when hepatic enzyme levels and bilirubin return to pretreatment values and only in patients who have not experienced clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Avoid initiation of FILSPARI in patients with elevated aminotransferases (>3x ULN) prior to drug initiation because monitoring hepatotoxicity in these patients may be more difficult and these patients may be at increased risk for serious hepatotoxicity.
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: FILSPARI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant patient and is contraindicated during pregnancy. Advise patients who can become pregnant of the potential risk to a fetus. Obtain a pregnancy test prior to initiation of treatment with FILSPARI, monthly during treatment, and one month after discontinuation of treatment. Advise patients who can become pregnant to use effective contraception prior to initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for one month after discontinuation of treatment with FILSPARI.
- FILSPARI REMS: Due to the risk of hepatotoxicity and embryo-fetal toxicity, FILSPARI is available only through a restricted program called the FILSPARI REMS. Prescribers, patients, and pharmacies must be enrolled in the REMS program and comply with all requirements (www.filsparirems.com).
- Hypotension: Hypotension has been observed in patients treated with ARBs and ERAs. There was a greater incidence of hypotension-associated adverse events, some serious, including dizziness, in patients treated with FILSPARI compared to irbesartan. In patients at risk for hypotension, consider eliminating or adjusting other antihypertensive medications and maintaining appropriate volume status. If hypotension develops, despite elimination or reduction of other antihypertensive medications, consider a dose reduction or dose interruption of FILSPARI. A transient hypotensive response is not a contraindication to further dosing of FILSPARI, which can be given once blood pressure has stabilized.
- Acute Kidney Injury: Monitor kidney function periodically. Drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) can cause kidney injury. Patients whose kidney function may depend in part on the activity of the RAS (e.g., patients with renal artery stenosis, chronic kidney disease, severe congestive heart failure, or volume depletion) may be at particular risk of developing acute kidney injury on FILSPARI. Consider withholding or discontinuing therapy in patients who develop a clinically significant decrease in kidney function while on FILSPARI.
- Hyperkalemia: Monitor serum potassium periodically and treat appropriately. Patients with advanced kidney disease, taking concomitant potassium-increasing drugs (e.g., potassium supplements, potassium-sparing diuretics), or using potassium-containing salt substitutes are at increased risk for developing hyperkalemia. Dosage reduction or discontinuation of FILSPARI may be required.
- Fluid Retention: Fluid retention may occur with ERAs, and has been observed in clinical studies with FILSPARI. FILSPARI has not been evaluated in patients with heart failure. If clinically significant fluid retention develops, evaluate the patient to determine the cause and the potential need to initiate or modify the dose of diuretic treatment then consider modifying the dose of FILSPARI.
Most common adverse reactions
The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) are hyperkalemia, hypotension (including orthostatic hypotension), peripheral edema, dizziness, anemia, and acute kidney injury.
Drug interactions
- Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Inhibitors and ERAs: Do not coadminister FILSPARI with ARBs, ERAs, or aliskiren due to increased risks of hypotension, syncope, hyperkalemia, and changes in renal function (including acute renal failure).
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use of FILSPARI with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, interrupt FILSPARI treatment. When resuming treatment with FILSPARI, consider dose titration. Monitor blood pressure, serum potassium, edema, and kidney function regularly when used concomitantly with moderate CYP3A inhibitors. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increases sparsentan exposure which may increase the risk of FILSPARI adverse reactions.
- Strong CYP3A Inducers: Avoid concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inducer. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inducer decreases sparsentan exposure which may reduce FILSPARI efficacy.
- Antacids and Acid Reducing Agents: Administer FILSPARI 2 hours before or after administration of antacids. Avoid concomitant use of acid reducing agents (histamine H2 receptor antagonist and PPI proton pump inhibitor) with FILSPARI. Sparsentan exhibits pH-dependent solubility. Antacids or acid reducing agents may decrease sparsentan exposure which may reduce FILSPARI efficacy.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (NSAIDs), Including Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Inhibitors: Monitor for signs of worsening renal function with concomitant use with NSAIDs (including selective COX-2 inhibitors). In patients with volume depletion (including those on diuretic therapy) or with impaired kidney function, concomitant use of NSAIDs (including selective COX-2 inhibitors) with drugs that antagonize the angiotensin II receptor may result in deterioration of kidney function, including possible kidney failure.
- CYP2B6, 2C9, and 2C19 Substrates: Monitor for efficacy of concurrently administered CYP2B6, 2C9, and 2C19 substrates and consider dosage adjustment in accordance with the Prescribing Information. Sparsentan decreases exposure of these substrates, which may reduce efficacy related to these substrates.
- P-gp and BCRP Substrates: Avoid concomitant use of sensitive substrates of P-gp and BCRP with FILSPARI. Sparsentan may increase exposure of these transporter substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
- Agents Increasing Serum Potassium: Monitor serum potassium frequently in patients treated with FILSPARI and other agents that increase serum potassium. Concomitant use of FILSPARI with potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, potassium-containing salt substitutes, or other drugs that raise serum potassium levels may result in hyperkalemia.
Please see the full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING, for additional Important Safety Information.
Are you a US healthcare professional?
The site you are about to enter is intended only for US healthcare professionals.



